Partnership deeds are frequently misunderstood by business owners, despite being foundational documents that determine how a partnership operates. Although starting a partnership requires just two partners, many entrepreneurs overlook crucial aspects of creating a legally sound deed, leading to complications later.
Despite the partnership deed's critical importance, business owners commonly make significant errors during its creation and registration. The deed should contain essential details like profit-sharing ratios, capital contributions, and partner roles, yet these elements are frequently omitted.
Furthermore, stamp duty requirements vary substantially across Indian states: Maharashtra charges Rs. 500 for capital up to Rs. 50,000 and 1% for amounts exceeding that (capped at Rs. 15,000). Importantly, using incorrect stamp paper values can render the entire partnership deed unenforceable in court.
While partnership deeds can technically be oral or written, a written agreement printed on non-judicial stamp paper worth at least Rs. 200 provides clarity and meets tax requirements. Additionally, business owners often don't realize that registration is governed by the Indian Registration Act, 1908, with LLP agreements requiring submission to the Registrar of Companies within 30 days of incorporation.
Read: Judicial vs Non Judicial Stamp Papers Guide
What Are the Basics Most Business Owners Overlook in Partnership?
Many entrepreneurs launch partnerships without understanding the fundamental legal document that governs their business relationship. A partnership deed is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions between partners, covering crucial elements like profit-sharing ratios, responsibilities, and operational rules.
What Is a Partnership Deed and Why Is It Not Optional?
A partnership deed serves as the foundation of a partnership firm, defining the agreement among members and establishing their roles, responsibilities, rights, and obligations. Primarily, it outlines essential details including the firm's name, partners' information, business nature, capital contributions, and profit-sharing arrangements.
What Happens Without a Partnership Deed?
Common misconception: Though not technically mandatory under the Indian Partnership Act of 1932, operating without a partnership deed is a significant oversight. Business owners often incorrectly assume verbal agreements suffice.
Read: What Is An Agreement ? Everything You Need To Know!
However, without this document, partners cannot:
- Use evidence to resolve disputes in court
- Enforce terms against third parties
- Claim tax benefits or deductions
- Sue each other or the firm during conflicts
Legal Enforceability and Tax Implications of a Partnership Deed
The legal status of a partnership deed significantly impacts business operations. An unregistered partnership deed remains valid between partners but has substantial limitations in legal contexts. Registration with the Registrar of Firms transforms the partnership into a separate legal entity that can enter contracts, sue, or be sued in its own name.
From a taxation perspective, a partnership deed is vital because:
- It defines profit-sharing ratios essential for determining each partner's taxable income
- It establishes eligibility for tax deductions under Indian tax laws
- It serves as legal proof of the partnership's structure for tax authorities
- It clarifies partner contributions and liabilities, affecting tax obligations
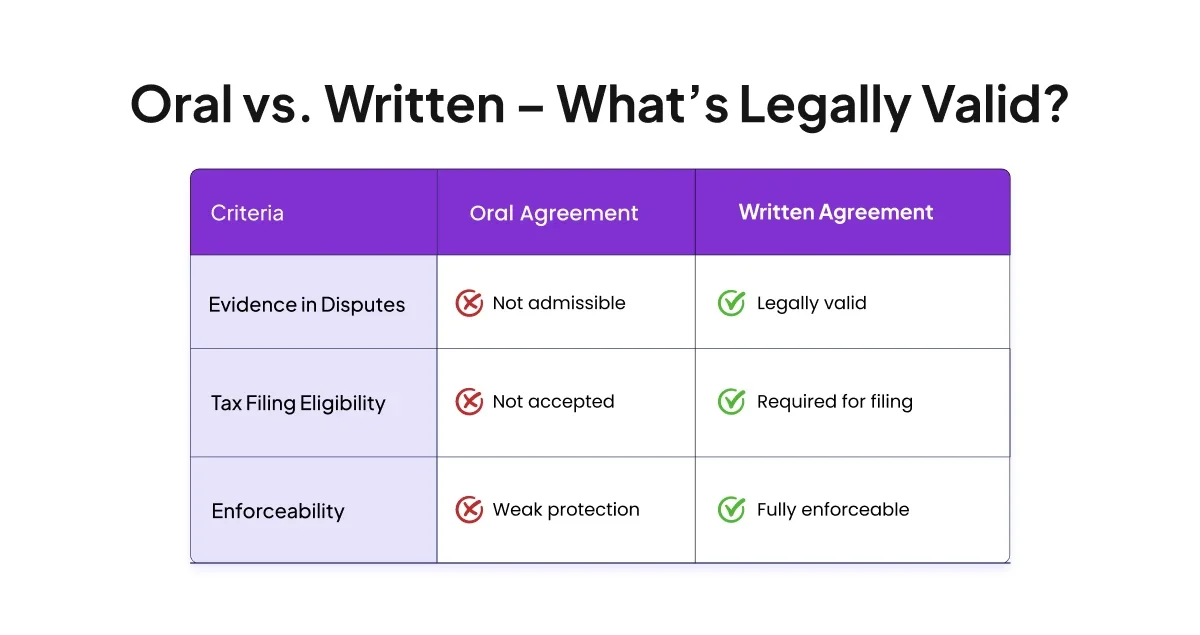
What Is the Difference Between Oral and Written Partnership Deeds?
Partnerships can technically form through oral or written agreements. However, the differences in practical application are substantial:
1. Oral agreements:
- Recognized under law but provide minimal protection
- Lack legal weight in disputes
- Cannot be used for tax purposes
- Difficult to prove terms agreed upon
2. Written agreements:
- Provide clear terms and conditions
- Serve as evidence during disputes
- Required for tax filings and benefits
- Essential for registration with authorities
For partnerships handling goods and services, a properly drafted deed ensures compliance with GST laws and specifies how related documents and filings are managed, reducing penalty risks.
Drafting the Deed in India: Where Most Business go Wrong
Drafting a partnership deed requires careful attention to detail, yet many business owners make critical errors that compromise the document's legal validity. The success of any partnership hinges on a well-drafted deed that clearly outlines rights, responsibilities, and agreed-upon terms among partners.
Risks of Using Outdated or Vague Partnership Deed Formats
One prevalent mistake is relying on generic templates found online without customizing them to specific business needs. These one-size-fits-all approaches fail to address the unique nature of each partnership. Consequently, many deeds contain ambiguous language leading to misunderstandings and disputes. A well-crafted partnership deed should use clear, specific terminology that leaves no room for misinterpretation.
Furthermore, partnership agreements often remain unchanged for years despite significant business evolution. As a firm grows, static agreements create friction and legal issues, especially during partner transitions. Regular reviews should occur annually or after significant changes such as new partners joining or shifts in practice focus.
Missing key clauses like Profit sharing or Exit terms
The omission of essential clauses represents another common pitfall. Many partnership deeds lack crucial elements including:
- Clearly defined profit and loss sharing ratios
- Comprehensive exit strategies for partners leaving the firm
- Decision-making mechanisms and dispute resolution procedures
- Capital contribution details and additional investment protocols
Without buy-sell provisions, remaining partners may face legal battles or financial strain when navigating uncertain terms during partner exits. Exit clauses should specify how a partner's interest will be valued, define buyout terms, and establish clear payout timelines to ensure fairness to all parties.
What Happens If There Is Improper Stamp Paper Usage?
Many business owners overlook stamp paper requirements for partnership deeds. The document must be printed on non-judicial stamp paper worth at least Rs.200, though values vary by state. Mumbai requires minimum Rs.500, while Bengaluru mandates Rs.500 if capital exceeds Rs.500.
Incorrect calculation of stamp duty or using inadequate stamp paper value renders the entire deed legally unenforceable in court. ZoopSign offers digital solutions to help you create legally compliant partnership deeds with up-to-date formats and all essential clauses, eliminating common drafting errors.
Remember that stamp duty payment delays can result in penalties, making timely compliance critical. Each state has different regulations, so understanding location-specific requirements prevents complications when formalizing your partnership agreement.
Read: Types of Stamps: Your Guide to Digital and Physical Options
Registration Process of Partnership Deed: Steps and Pitfalls
The registration process for partnership deeds often confuses business owners who face a maze of requirements varying by state. Understanding the correct procedure helps avoid legal complications and preserves the firm's ability to enforce its rights.
How to Register a Partnership Deed Correctly?
Registration of a partnership firm, while not mandatory under the Indian Partnership Act of 1932, provides significant legal protection. To register correctly:
- Draft a comprehensive partnership deed on appropriate stamp paper
- Submit Form 1 (application) to the Registrar of Firms in your state
- Include details like firm name, principal business address, names of all partners, and profit-sharing arrangement
- Pay the prescribed registration fees
- Obtain the Certificate of Registration after verification
What Documents Are Required in Partnership Deed Registration?
Here are the Required documents that include:
- Partnership deed (certified by CA/Advocate)
- Application form with court fee stamp
- Identity and address proof of all partners
- Proof of principal place of business
What Are Common Errors in Registration?
Common errors include using incorrect stamp paper values, inconsistent partner details across documents, and failing to get proper notarization. Other mistakes involve submitting applications beyond the one-month deadline after notarization or using stamp papers older than six months.
What Are the State-Wise Stamp Duty Variations for Partnership Deeds?
Stamp duty requirements vary significantly across India.
1. Mumbai requires minimum Rs.500,
2. Bengaluru mandates Rs.500 if capital exceeds Rs.500, and
3. Delhi requires a minimum Rs.200.
4. In Gujarat, it's 1% of partnership capital (maximum Rs.10,000), while
5. Maharashtra charges 1% (maximum Rs.15,000).
What happens if you skip registration of a Partnership Deed?
Unregistered partnerships face serious limitations:
- Cannot file lawsuits against third parties
- Partners cannot sue each other or the firm
- Cannot claim set-offs exceeding Rs.100 in legal proceedings
- Remain vulnerable to third-party lawsuits without full defense options
- Ineligible for certain government contracts and tenders
- Reduced credibility with banks and financial institutions
How to Fix Mistakes and Stay Compliant with Partnership Deed Regulations?
Even after registration, partnership deeds sometimes need corrections. Errors or omissions can lead to legal complications if not addressed properly and promptly.
How to Rectify Errors in Registered Deeds?
Under Section 64 of the Indian Partnership Act, the Registrar has authority to rectify mistakes in partnership records. For corrections of spelling errors or omissions, signatures of all existing partners are required on the rectification application.
Nevertheless, a letter authorizing representation at personal hearings can be signed by just one partner. The process involves submitting an application with documentary proof and paying fees of Rs.1000 plus Rs.200 for documentation.
When Should You File Form B, D, or E for Partnership Deed Changes?
Different forms serve specific purposes in maintaining accurate partnership records:
- Form B/D: Required when changing the firm's address. Even if a new address appears in a supplementary deed, Form B or D must be filed to officially notify the change.
- Form D: Used specifically for changes in partner details. For a female partner whose name and address change due to marriage, Form D must be filed within 90 days along with an attested marriage certificate.
- Form E: Necessary for constitutional changes like partner additions or exits. Also required when reporting a change in HUF Karta, accompanied by a death certificate if applicable.
What Tips Help Avoid Registrar Objections During Partnership Deed Registration?
- Ensure stamp papers are in the firm's or partners' names
- File documents within one month of notarization
- Verify stamp paper dates are within six months of deed execution
- Secure notary seals in red ink with initials on all pages
- Submit both Form E and Form B/D for simultaneous changes in constitution and address
How to Maintain Updated Records with the Registrar of Firms?
Regular updates with the Registrar of Firms prevent legal complications and ensure business continuity. ZoopSign's digital document management system helps you maintain updated partnership records, easily rectify errors, and stay compliant with registrar requirements. For third-party submissions, include an authority letter signed by all partners.
Always match deed particulars with information in the forms and compare with the last recorded entry to maintain consistency across all documentation.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS:
1. What is a partnership deed and why is it important?
A partnership deed is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions between partners in a business. It's crucial because it defines roles, responsibilities, profit-sharing arrangements, and other essential aspects of the partnership. Without a proper deed, partners may face difficulties in resolving disputes, enforcing terms, and claiming tax benefits.
2. Is registering a partnership deed mandatory?
While registration is not mandatory under the Indian Partnership Act of 1932, it's highly recommended. An unregistered partnership faces limitations such as inability to file lawsuits against third parties, restrictions on partners suing each other or the firm, and ineligibility for certain government contracts and tenders.
3. What are common mistakes in drafting a partnership deed?
Common errors include using outdated or vague templates, omitting key clauses like profit-sharing ratios and exit terms, and improper stamp paper usage. These mistakes can render the deed legally unenforceable and lead to disputes among partners.
4. How does stamp duty for partnership deeds vary across states?
Stamp duty requirements differ significantly across Indian states. For example, Mumbai requires a minimum of Rs. 500, while Delhi mandates at least Rs. 200. In some states, the duty is calculated as a percentage of the partnership capital, with maximum limits. It's crucial to understand and comply with location-specific requirements to ensure the deed's validity.
5. How can errors in a registered partnership deed be rectified?
Errors in registered partnership deeds can be corrected by submitting an application to the Registrar of Firms under Section 64 of the Indian Partnership Act. This process typically requires signatures from all existing partners, documentary proof, and payment of prescribed fees. Different forms (like Form B, D, or E) may need to be filed depending on the nature of the change or correction.