Are you confused about what an e-auction in India really means? You’re not alone.
Imagine that you’ve just placed the highest bid on a prime property in an e-auction and won. Feels like victory, right? Not quite. That winning bid is just a receipt — not proof of ownership. Until the right stamp is affixed on the right paper, the property isn’t legally yours. In India’s high-stakes e-auction landscape, the real win begins only after the hammer falls.
This guide cuts through the confusion around non-judicial stamp paper, online stamp duty payment, and legal compliance. We’ll show you how to turn your winning bid into undisputed ownership—and what happens if you get it wrong.
What Does an E-Auction in India?
An e-auction is a fully digital process where assets are sold to the highest bidder through an online platform, eliminating the need for physical presence while ensuring transparency and wider participation.
Here’s how it works:
1. Digital Bidding: It happens entirely online through dedicated platforms. You bid from your phone or laptop. No crowded rooms or paper paddles.
2. Transparent Process: Every bid is visible, reducing manipulation. You see who’s bidding and how much, in real-time.
3. Simple Steps:
- Sellers list items with details, photos, and a start price.
- Buyers register (often with a refundable security deposit).
- Bidding opens.
- The highest bid when time runs out wins.
- The system notifies the winner automatically.
While winning the bid is a key milestone, the process isn’t complete until the supporting legal documents, like the sale certificate, are properly stamped.
Overlooking this step can instantly invalidate the transaction
Why Is Stamp Duty Essential for E-Auction Property Ownership?
Paying stamp duty is what makes your e-auction win, legally binding and officially transfers ownership of the asset to you.
Treating it as an optional formality can invalidate your entire purchase.
Think of it as the government’s seal of approval on your transaction. Without it, your document holds no weight in court, offers no proof of ownership, and leaves you financially exposed.
Here’s what happens if you get it wrong:
- Your Document Becomes Useless: An unstamped sale certificate is not admissible as evidence in court. If someone challenges your ownership, you have no legal leg to stand on.
- You Invite Penalties: Miss the strict 30-day payment window, and you’ll face hefty fines from the state on top of the original duty amount.
- You Risk Fraud: While traditional stamps could be faked, e-stamp paper offers a secure, verifiable record. Skipping it means losing this protection.
Getting the stamp duty right is the starting point of your true ownership. And doing it right starts with understanding the very tool designed for it: e-stamp paper.
What Is E-Stamp Paper and How Has It Changed E-Auctions?
E-stamp paper is a secure, government-approved digital certificate that replaces physical stamp paper, making stamp duty payment for e-auction wins faster, tamper-proof, and entirely online.
It’s the modern solution to a historically cumbersome process.
Gone are the days of hunting for authorized vendors or worrying about fake stamps. Understanding the different types of stamp papers available is key to navigating this process correctly. E-stamping, managed by authorized providers like the Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL), cuts through the clutter and brings stamping into the digital age.
Here’s how it has specifically improved the auction process:
- Eliminates Fraud & Counter Security Risks: Each e-stamp has a unique transaction reference number (TRN) and is tamper-proof. This kills the risk of counterfeit stamps that could invalidate your auction purchase.
- Adds Speed & Convenience: You can generate an e-stamp certificate 24/7 from anywhere, in minutes. There’s no need to visit government offices or vendors, which is crucial for meeting the tight deadlines after winning an auction.
- Ensures Transparency & Easy Verification: The system provides real-time validation. Authorities can instantly verify the authenticity of your stamp duty payment, preventing legal disputes down the line.
- Streamlines Record-Keeping: Everything is digital. You can easily download and store your e-stamp certificates, maintaining a secure audit trail for all your legal and financial records.
By making stamp duty payment secure and instant, e-stamp paper removes a major friction point from the e-auction journey.
Read more: For a deeper dive into its benefits and uses, check out our complete guide to e-stamping.
Now, let’s walk through the exact steps to pay this duty correctly.
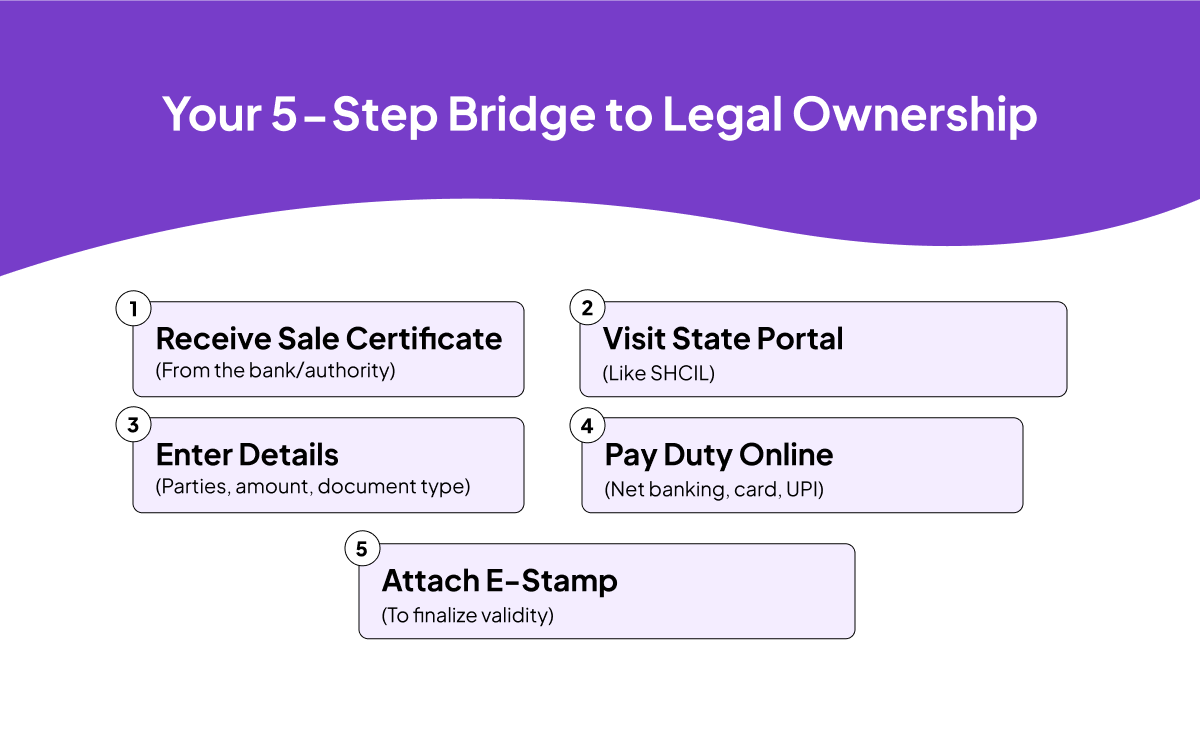
What Are the Steps to Pay Stamp Duty After Winning an E-Auction?
Paying stamp duty after winning an e-auction is a non-negotiable online process that legally validates your Sale Certificate. Without it, your winning bid is just an expensive piece of paper.
Here’s the straightforward process to secure your ownership:
- Get Your Sale Certificate: The auction authority (like a bank) issues this document after you win and pay the full amount. This is what needs stamping.
- Head to the Official Portal: Go to your state’s e-stamping portal (often SHCIL).
- Enter the Details: Fill in the form. This includes the document type (Sale Certificate), party names, and your winning bid amount.
- Pay the Calculated Duty: The portal auto-calculates the duty. Pay it online via net banking, card, or other digital methods.
- Attach the Proof: Download the e-stamp certificate and securely attach it to your Sale Certificate. This finalizes its legal validity.
Think of this as the final administrative hurdle that transforms your auction win into undisputed legal ownership.
For businesses managing multiple transactions, this manual process can be streamlined with platforms like ZoopSign that offer Pan-India coverage and automated procurement from a single dashboard.
Who Is Responsible for Paying Stamp Duty and Registration After E-Auction?
The winning bidder is solely responsible for paying both stamp duty and registration charges after a successful e-auction.
Think of it as the final, non-negotiable premium on your winning bid. The "as-is, where-is" clause in auction agreements isn't subtle about this: all statutory costs fall on you, the purchaser. These charges are calculated on the final hammer price or circle rate (whichever is higher), and missing the payment window doesn't just delay ownership, it risks invalidating your entire purchase.
Now that you know this crucial financial responsibility falls on you, the immediate next step is to ensure that your payment translates into legally valid proof.
How Can You Verify and Use Your E-Stamp Certificate?
E-stamp certificate verification confirms the authenticity of your digital stamp duty payment through official channels like the SHCIL portal, while proper usage ensures your document remains legally valid and enforceable.
After winning an e-auction, your e-stamp certificate requires two critical actions: verification to confirm its authenticity, and physical application to complete the legal transfer.
Here’s how you can verify your e-Stamp certificate:
- Use the SHCIL Portal: Visit the official SHCIL website or mobile app, select 'Verify eStamp', and enter your certificate's unique Certificate Number, Issue Date, and Session ID.
- QR Code Verification: Scan the QR code on your certificate using your smartphone for instant authentication against government records.
- Confirm Details: Ensure the verification results match your certificate's details exactly, including the stamp duty value and parties involved.
Now, using your verified e-stamp certificate correctly is equally important.
Once authenticated, you must print the certificate and physically attach it to your sale deed or agreement. The document should be signed by all parties, with signatures crossing from the main document onto the attached stamp certificate.
This process creates a single, legally binding instrument that courts will recognize as valid. Proper attachment and execution transform your agreement into an enforceable contract that completes the ownership transfer from your e-auction win.
Verification takes minutes but protects you from fraud, while correct physical application ensures your document will withstand legal scrutiny.
With your document properly verified and executed, it's now important to understand its legal standing and stay informed about regulatory changes affecting e-stamp validity.
What Is the Legal Validity of E-Stamp Paper for E-Auctions in India?
E-stamp certificates issued through authorized portals like SHCIL hold full legal validity under the Indian Stamp Act, 1899, and recent judicial updates have significantly clarified their application in e-auction transactions, particularly regarding sale certificates.
The legitimacy of e-stamping isn't up for debate. It's explicitly recognized across Indian states as a secure, legally equivalent alternative to physical stamp papers.
However, staying updated on judicial interpretations is critical, because they directly impact your compliance and risks.
1. Legal Validity
- Admissibility in Court: Properly verified e-stamp certificates are fully admissible as evidence in legal proceedings, just like physical stamps. An unstamped or improperly stamped document will be rejected by courts and cannot be enforced.
- Governing Laws: The Indian Stamp Act, 1899, and state-specific stamping rules provide the foundation for e-stamp validity. The IT Act, 2000, further supports the digital authentication and integrity of these certificates.
- Universal Recognition: All government authorities, financial institutions, and judiciary bodies accept e-stamps for property transactions, agreements, and affidavits.
2. Recent Updates
- Sale Certificate Clarification: The 2024 Supreme Court ruling (State of Punjab v. M/s Ferrous Alloy Forgings) clarified that sale certificates from court-directed auctions don't automatically attract stamp duty. However, if used for registration or other formalities, duty becomes payable immediately.
- State-Level Expansions: States like Maharashtra and Karnataka have streamlined e-stamping integrations, reducing payment windows from 30 days to 15-20 days for faster transaction closures.
- Anti-Fraud Measures: Enhanced QR code encryption and unique cryptograms are now mandatory on e-stamp certificates to prevent forgery in high-value e-auctions.
Navigating e-auctions requires more than just the highest bid. It demands compliance with evolving stamp duty regulations.
Getting it right protects your investment, whereas getting it wrong risks everything you've paid for.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How much is the stamp duty on property e-auctions in India?
A: Stamp duty rates vary by state and are calculated on either your final winning bid amount or the property's circle rate, whichever is higher. There is no fixed national rate, so you must check your specific state's stamp duty regulations.
Q: Is e-stamp paper mandatory for all e-auctions?
A: While physical stamp papers are still technically accepted in some regions, e-stamp paper is the recommended and secure standard for e-auctions. It provides legal validity, reduces fraud risk, and ensures your documents will be accepted in court and by government authorities.
Q: How can I check if my e-stamp certificate is genuine?
A: Verify your e-stamp certificate through the official SHCIL portal or mobile app by entering your certificate details, or simply scan the QR code on the certificate using your smartphone for instant authentication against government records.
Q: Can stamp duty be refunded if the e-auction sale is cancelled?
A: The provided content doesn't specify refund policies for cancelled e-auction sales. Please share relevant source material on stamp duty refund procedures, and I'll provide an accurate answer based on that information.
Q: What documents are needed for e-auction property transfer?
A: The essential documents are the Sale Certificate issued by the auction authority and the corresponding e-stamp certificate proving stamp duty payment. These must be physically attached together and signed across both documents to complete the legal transfer process.